Media Center
A multimedia mosaic of moments at GIST
GIST Excellence
[Press release] Professor Hyunju Lee"s research team develops cancer-related microRNA ranking methodology
- 엘리스 리
- REG_DATE : 2016.12.13
- HIT : 954
Professor Hyunju Lee"s research team develops
cancer-related microRNA ranking methodology
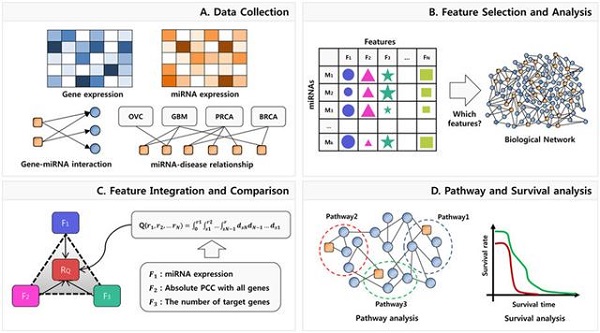
[Figure 1] Methodology summary: (a) Gene and microRNA expression and microRNA and disease (cancer) relationship information are collected. (B) Analyze and identify features associated with cancer. (C) Compute the aggregated scores of the selected features on a sequence-based method, and rank the microRNAs. (D) Biological pathway analysis and survival time analysis are performed on cancer-associated microRNAs.
□ Professor Hyunju Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) has developed a methodology to rank microRNAs that are highly related to cancer. The developed methodology is expected to contribute to the discovery of available microRNAs in cancer diagnosis and treatment.
* MicroRNA: A small RNA molecule composed of 20 to 22 nucleotides. It binds to the 3" untranslated region of other genes to form a complementary sequence and controls the expression of the gene. In particular, it plays an important role in inhibiting carcinogenesis genes and cancers, so it is used as an important biomarker in cancer diagnosis and prognosis.
The researchers identified the features of cancer-associated microRNAs and used order statistics * to rank cancer-associated microRNAs.
* Sequence statistics: The samples are taken and sorted in size order. The measured values x1, x2, x3, ..., xn of random samples of size n are arranged in order of small value to large value. It may also be expressed as x (1), x (2), x (3), ..., x (n) In a broad sense, the function of x (1), x (2), x (3), ..., x (n) is called a sequence statistic .
The researchers first determined the expression levels of microRNAs, the expression level of messenger RNA, and the similarity of sequence from cancer data obtained from individual cancer cells to characterize cancer-related microRNAs.
They then developed a method to rank the microRNAs based on the integrated score of features using the sequential statistics technique.
The team applied the methodology to brain tumors, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, and breast cancer samples to identify and rank important microRNAs for each cancer. As a result, high-ranking microRNAs have been shown to be highly correlated with cancer, and low-ranking microRNAs have little relevance to cancer. Compared to the existing methodologies, it demonstrated much better performance in finding microRNAs that are highly related to cancer.

□ Professor Hyunju Lee said, "The developed methodology is expected to be widely used to identify key micro-RNAs that are related to various cancers."
The research was supported by the GIST Research Institute (GRI) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). The paper was published in Scientific Reports on October 13, 2016.