Media Center
A multimedia mosaic of moments at GIST
GIST Excellence
[Press release] Professor Chun T. Rim focuses high-resolution magnetic fields
- 엘리스 리
- REG_DATE : 2016.11.15
- HIT : 999
Professor Chun T. Rim focuses high-resolution magnetic fields

(Image 1). Synthesized magnetic field generation experiment device. Ten coils are placed at a constant interval of 5 cm)on the ferrite core, which is a black magnetic material, and the magnetic field is strongly focused at a point 10 cm away from the current calculated by the equation developed by Professor Rim.
□ Domestic researchers have succeeded in overturning the stereotype that magnetic fields generated by magnets are always spreading, and they have proposed the possibility of applying this new approach to medical device development, disease treatment, and underground detection.
∘ Professor Chun T. Rim of the Energy Convergence Interdisciplinary Graduate School at the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) was the first in the world to create a magnetic field generated from several current sources arranged in parallel in order to concentrate the magnetic fields in arbitrary directions and positions.
∘ Professor Rim recently published a paper * in IEEE Magnetics Letters, which is published by the prestigious International Electrical and Electronics Engineering Society, and he participated in the annual seminar held at Samsung Electronics Future Technology Development Center on November 10, 2016.
* Title: Synthesized Magnetic Field Focusing Using a Current-Controlled Coil Array
□ The magnetic field is a basic physical field that is widely used for magnetic resonance devices, wireless power, proximity communication, nondestructive inspection, material exploration, etc. depending on the frequency.
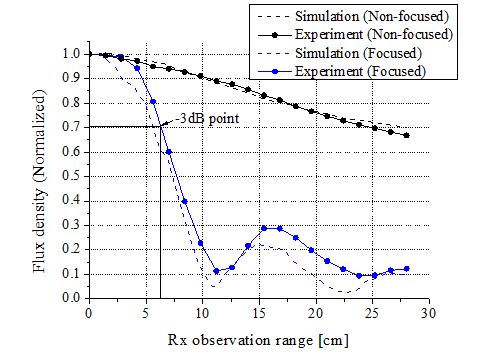
(Image 2). Graph showing the results of magnetic field density measurement when the magnetic field is focused and when it is not focused. The black graph shows the magnitude of the magnetic field generated by the current flowing in one coil by the side distance, and the blue shows that the magnetic field is synthesized by the currents of 10 coils to obtain a magnetic field graph with a sharp gradient of about 4 times.
The researchers fabricated 10 different current sources by winding a rectangular ferrite core around the magnetic ferrite core, and at a magnetic field density of 1.5 milliseconds * (mT) at a distance of 10 cm therefrom and succeeded in obtaining a magnetic field.
* Millitesla: The value of 1 / 1000th of Tesla, the basic unit of the magnetic field.
The researchers found that as the number of current sources increases, higher focusing resolutions can be obtained and the direction and position of the focused magnetic field can be changed arbitrarily by changing the value of the current source appropriately.
∘ Unlike a phased array antenna that uses radio waves, it can focus a magnetic field irrespective of frequency or phase, and it can be used from DC to high frequency AC.
□ Professor Chun T. Rim said, "Applying the principle of focusing magnetic field obtained from this study, it is possible to develop self-medical imaging device, treatment of cerebral infarction by local induction heating, cancer treatment, and underground cavity or underground metal detection."
∘ This study was supported by Samsung Electronics Future Technology Development Center with 800 million won for three years.