Media Center
A multimedia mosaic of moments at GIST
GIST Excellence
[Press Release] GIST Professor Hyunju Lee has led a research team to develop a wavelet-based method to identify cancer-driver genes
- 엘리스 리
- REG_DATE : 2016.05.27
- HIT : 840
GIST Professor Hyunju Lee has led a research team
to develop a wavelet-based method to identify cancer-driver genes
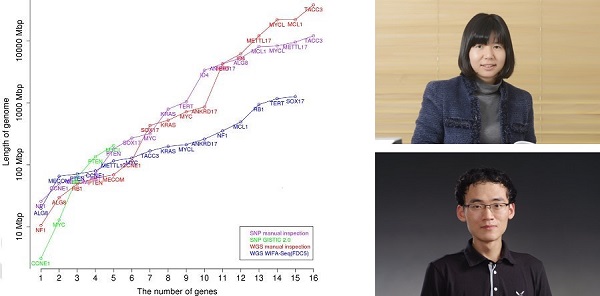
Figure 1. Comparison between manual inspection and WIFA-Seq for GBM. The x-axis represents the number of known GBM genes, and the y-axis represents the length of the genomes for identifying the genes. For the y-axis, the accumulated length of clusters sorted by their scores was used for WIFA-Seq, and the accumulated length of the segments sorted by the log2 ratio values of the segments was used for the manual inspection. The red and blue lines represent the costs of manual inspection and WIFA-Seq, respectively.
Next generation sequencing (NGS) for DNA has revolutionized genomic science with the ability to sequence 1.8 terabases of data in a single run, allowing scientists to sequence 45 human genomes in a single day at a cost of about $1,000 per person. When compared to the first human genome which took 15 years to sequence at a cost of 3 billion dollars, the amount of genetic data produced by NGS is astronomical, and meaningful analysis of that such prodigious amounts of data is a daunting task.
To more efficiently identify cancer-driver genes among the data produced by NGS, a research team led by GIST Professor Hyunju Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science has developed a wavelet-based method called WIFA-Seq for identifying focal genomic alterations for sequencing data. DNA copy number alterations are the main genomic events that occur during the initiation and development of cancer, and being able to distinguish driver aberrant regions from passenger regions is an important issue for cancer therapies.
Their paper entitled "Identification of cancer-driver genes in focal genomic alterations from whole genome sequencing data" was published on May 9, 2016, in Scientific Reports and was authored by Ho Jang, Youngmi Hur, and Hyunju Lee.
Professor Hyunju Lee said, "This algorithm is expected to be widely used to find genetic variations associated with cancer within data produced by NGS."